HotConnect, Repair, and Restart
In this section, we describe how HotConnect, Repair, and Restart work and we provide a few cases.
HotConnect
HotConnect is the process of adding hardware using extra EtherCAT-enabled ports, such as Ethernet (ports on T-junctions and couplers), eBUS (connectors on couplers), and M12 (round connectors on waterproof devices). This way, new devices can be added without interrupting the operation of existing hardware. You can add hardware in the beginning or among devices. However, adding a device in the beginning requires the EtherCAT connection to be restarted, as you need to unplug the cable connected to the computer and all devices will be offline, unless you use cable redundancy. Interrupting other devices is not the purpose of HotConnect. Typically, new hardware is added at the end or among devices. Because KINGSTAR uses indexes to sort devices, new hardware is always put at the end of the EtherCAT slave list, and its index is incremented from the last existing device.
Function: EnableHotConnect
When enabled, you can add new hardware while an EtherCAT network is running. When disabled, you need to add hardware when it is stopped.
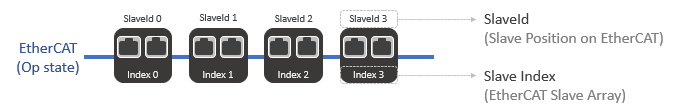
NOTE: When EtherCAT is started, the slave index has the same value as the SlaveId, which corresponds to the position of the slave in the network. After EtherCAT is started in the Operational (Op) state, any addition or removal of slaves from the network will change the position of the slaves in the network (SlaveId). Nevertheless, the index of the slave will remain the same. Newly added devices will be added in the back of the slave array. For all slaves after the change, the index and SlaveId will no longer match. This behavior is only available for physical devices; simulated devices are inapplicable. Please refer to the following use cases for more details.
Use case 1
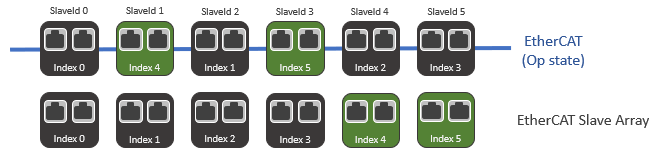
Adding a device when HotConnect is enabled
There are four servo drives connected to the EtherCAT. If we connect devices with SlaveId 1 and SlaveId 3 to the EtherCAT, these two devices will be recognized as Index 4 and Index 5 in the Index array, respectively. The original Index 1, Index 2, and Index 3 on the EtherCAT remain unchanged in their indexes; however, their SlaveIds will be changed to reflect their new positions.
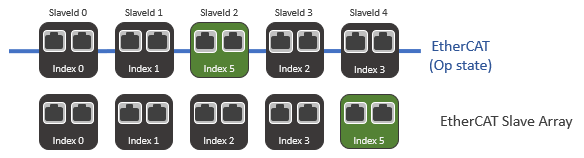
Removing a device when HotConnect is enabled
Continuing from the above case, if we remove Index 4 from the EtherCAT, the SlaveId of the devices connected behind Index 4 will be changed to reflect their new positions.
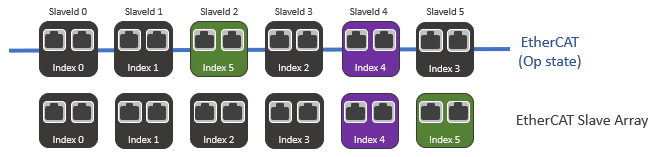
Reconnecting a device to a different position when HotConnect is enabled
Continuing from the above case, if we reconnect Index 4 back to the EtherCAT in a different position (SlaveId 4), its Index will still be Index 4.
Use case 2
HotConnect is enabled. There are four servo drives and we want to add two additional drives between the third and fourth. We have a T-junction, so we can add the drives using extra Ethernet ports. In KINGSTAR, the indexes of the newly added devices are four and five (indexes are zero-based), and the new drives appear at the end of the EtherCAT slave list.
Repair
The feature replaces a broken hardware or cable with a new one while all other devices — and the EtherCAT network — are running, and it repairs the EtherCAT state of the new device to Operational (Op). You must use the same model to replace the old one, because EtherCAT applies the old model's settings to the new model. If you have a model that has the same Vendor ID and Product Code as the old one, and is compatible with the old one's settings, you can use it.
Function: EnableAutoRepair
When enabled, the EtherCAT states of the new device and all the hardware behind it will be changed to Op automatically. When disabled, their states will be Init, and you will need to change them to Op manually. To manually change the state, use RequestSlaveState.
Use case
AutoRepair is enabled. There are five servo drives and we want to replace the third one. We unplug the cable between the second and the third. The hardware from the third to the final drive are offline. We replace the third with a same model and plug the cable back in. The EtherCAT states of the third and all the devices behind it are Init at first, and then proceed to Op.
Repair + HotConnect
Repair is used to replace a device with the same model, which must have the same Vendor ID and Product Code. HotConnect is used to add new devices. If the Vendor ID or Product Code of the new device is different from the previous one, HotConnect is used. When they are the same, Repair is used.
Use case
AutoRepair and HotConnect are enabled. There are five servo drives and we want to add two between the third and fourth. We don't have a T-junction or coupler, so we have to unplug the cable connecting the third and fourth. The fourth and fifth are offline. We connect the two drives and plug all the cables back in. All the offline drives are online and their states are changed to Op.
In this case, the original fourth and fifth drives use AutoRepair because they are the same models. The two new drives use HotConnect.
Restart
As the name implies, it restarts the EtherCAT master when the cable connected to the computer is unplugged and then plugged back in.
Function: EnableAutoRestart
When enabled, the EtherCAT master is restarted automatically when the cable is plugged back in. When disabled, it won't be restarted automatically. To manually start or restart them, use Start or Restart.
Use case
AutoRestart is enabled. There are five devices and the cable connected to the computer is loose. We plug it back in and all the devices are restarted.
Start and Restart
Start scans the devices on an EtherCAT network while Restart doesn't. Because of this, Start is slower than Restart. If you have added new hardware without HotConnect, you need to use Start.
See also
RT and Win32 – KINGSTAR Fieldbus - Subsystem configuration
RT and Win32 – KINGSTAR Fieldbus - Subsystem control
.NET API – Api Class - Subsystem configuration
.NET API – Api Class - Subsystem control
.NET Class – ISubsystem Interface - Methods
.NET Class – ISubsystem Interface - Properties