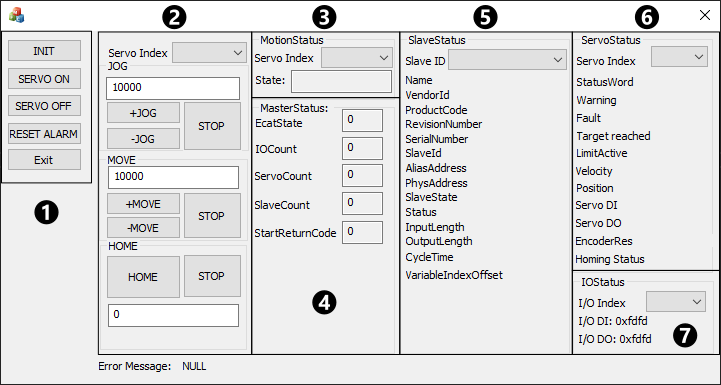
Main menu
Controls the interaction between the KINGSTAR Subsystem and an axis.
INIT: connects or disconnects the KINGSTAR Subsystem.
SERVO ON: enables an axis.
SERVO OFF: disables an axis.
RESET ALARM: resets the alarm of an axis.
Exit: exits Motion Sample.
Motion control
This area contains the settings for axes. It provides the basic motion that can be used to test axes.
Servo Index: the index of an axis (servo motor). The index is zero-based. This index is sorted by the order of the servo drives on the EtherCAT network. For example, you have eight EtherCAT slaves. Each servo drive has one axis. The following is their order:
- Servo drive – Slave ID: 0 – Servo Index: 0
- Servo drive – Slave ID: 1 – Servo Index: 1
- I/O module – Slave ID: 2 – I/O Index: 0
- I/O module – Slave ID: 3 – I/O Index: 1
- Servo drive – Slave ID: 4 – Servo Index: 2
- Servo drive – Slave ID: 5 – Servo Index: 3
- I/O module – Slave ID: 6 – I/O Index: 2
- I/O module – Slave ID: 7 – I/O Index: 3
In a complicated case, a servo drive has two or more axes. The order is like this:
- Servo drive – Slave ID: 0 – Servo Index: 0
- Servo drive – Slave ID: 1 – Servo Index: 1, 2, 3, 4
- I/O module – Slave ID: 2 – I/O Index: 0
- I/O module – Slave ID: 3 – I/O Index: 1
- Servo drive – Slave ID: 4 – Servo Index: 5
- Servo drive – Slave ID: 5 – Servo Index: 6
- I/O module – Slave ID: 6 – I/O Index: 2
- I/O module – Slave ID: 7 – I/O Index: 3
If you add simulated axes, they'll be contained in the Servo Index list too. The indexes of simulated ones are after those of real ones.
Jog
Makes a jog move.
Text box: the jog's velocity.
+JOG: the motor runs forwards.
-JOG: the motor runs backwards.
STOP: stops the jog motion.
MOVE
Makes a MoveAxisRelative move.
Text box: the move's distance.
+MOVE: the motor runs forwards.
-MOVE: the motor runs backwards.
STOP: stops the relative move.
HOME
Moves an axis to a known position.
HOME: moves an axis to a known position.
STOP: stops homing.
Text box: the homing mode provided by an axis.
MotionStatus
Servo Index: the index of an axis.
State: the state of an axis. See the McMotionState type.
MasterStatus
The state of the EtherCAT master. See the SubsystemStatus structure for the descriptions. For more information about StartReturnCode, see Startup errors in the KsError type.
SlaveStatus
The state of an EtherCAT slave. See the SlaveStatus structure for the descriptions.
Slave ID: the EtherCAT ID of a device. It corresponds to the position of the device in the EtherCAT loop. The ID is zero based and is not affected by aliasing.
ServoStatus
The state of an axis.
Servo Index: the index of an axis.
StatusWord to LimitActive: the CANopen states.
Velocity to Homing status: these parameters varies between servo motors.
I/OStatus
I/O Index: the index of an I/O module. The index is zero-based and sorted by the order of the I/O modules on the EtherCAT network. For more information about the index order, See Motion control.
If you add simulated I/O modules, they'll be contained in the I/O Index list too. The indexes of simulated ones are after those of real ones.
I/O DI: the digital input of the I/O module.
I/O DO: the digital output of the I/O module.