Main function
In this section, you'll learn how to apply all the code in this chapter to main.cpp. If everything is done correctly, you should be able to read and write real and simulated I/O modules. To help you review what you have learned, we add comments into the code to describe the meaning of the functions.
- In
main.cpp, under#include "SystemInitialization.h", add the following code: - In
int _tmain, under the code blockif (!StartKingstar()), add the following code to get the number of devices on your EtherCAT network. - Under
RtPrintf("\n");, add the following code to read and write data into I/O modules. The values we give for the functions are examples. You can fill the values depending on your needs.
#include "IOModule.h" //Create an instance of the SubsystemStatus structure and get the state from it.
SubsystemStatus Subsystem = { ecatOffline, ecatOffline, 0, 0, 0, {ecatOffline}, {ecatOffline}, {axisOffline} };
GetStatus(&Subsystem, NULL);
//Display the details of the EtherCAT network.
RtPrintf("Number of Devices found: %d\n", Subsystem.SlaveCount);
RtPrintf("Number of Axes found: %d\n", Subsystem.AxesCount);
RtPrintf("Number of I/O found: %d\n", Subsystem.IOCount);
RtPrintf("\n");NOTE: To use both real and simulated I/O modules, the number in SetConfiguredIoCount must be greater than the number of real I/O modules. See Chapter 2 > Start the KINGSTAR Subsystem, step 4.
//Display the length of the inputs and outputs of all I/O modules.
GetAllInputsOutputs();
//Write TRUE to the fourth I/O module, offset zero.
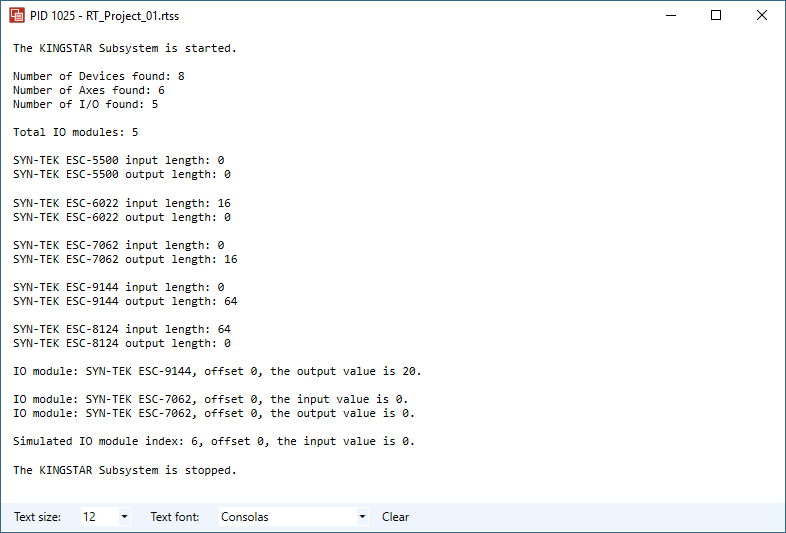
WriteReadOutput(3, 0, 20);
//Read the value from the third I/O module, offset zero.
ReadInputOutput(2, 0);
//Write a value into a simulated I/O module, offset zero.
ForceInput(6, 0, 8);Complete code
In conclusion, in main.cpp, your code should be as follows:
#include "RT_Project_01.h"
#include "SystemInitialization.h"
#include "IOModule.h"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR * argv[])
{
//Start the KINGSTAR Subsystem.
if (!StartKingstar())
{
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is not started.\n");
return -1;
}
else
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is started.\n");
RtPrintf("\n");
//Create an instance of the SubsystemStatus structure and get the state from it.
SubsystemStatus Subsystem = { ecatOffline, ecatOffline, 0, 0, 0, {ecatOffline}, {ecatOffline}, {axisOffline} };
GetStatus(&Subsystem, NULL);
//Display the details of the EtherCAT network.
RtPrintf("Number of Devices found: %d\n", Subsystem.SlaveCount);
RtPrintf("Number of Axes found: %d\n", Subsystem.AxesCount);
RtPrintf("Number of I/O found: %d\n", Subsystem.IOCount);
RtPrintf("\n");
//Display the length of the inputs and outputs of all I/O modules.
GetAllInputsOutputs();
//Write TRUE to the fourth I/O module, offset zero.
WriteReadOutput(3, 0, 20);
//Read the value from the third I/O module, offset zero.
ReadInputOutput(2, 0);
//Write a value into a simulated I/O module, offset zero.
ForceInput(6, 0, 8);
//Stop the KINGSTAR Subsystem.
if (!StopKingstar())
{
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is not stopped.\n");
return -1;
}
else
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is stopped.\n");
return 0;
}NOTE: To let you easily understand how to read and write I/O modules, we leave only necessary code in the main function. It's up to you to add more.
Output: