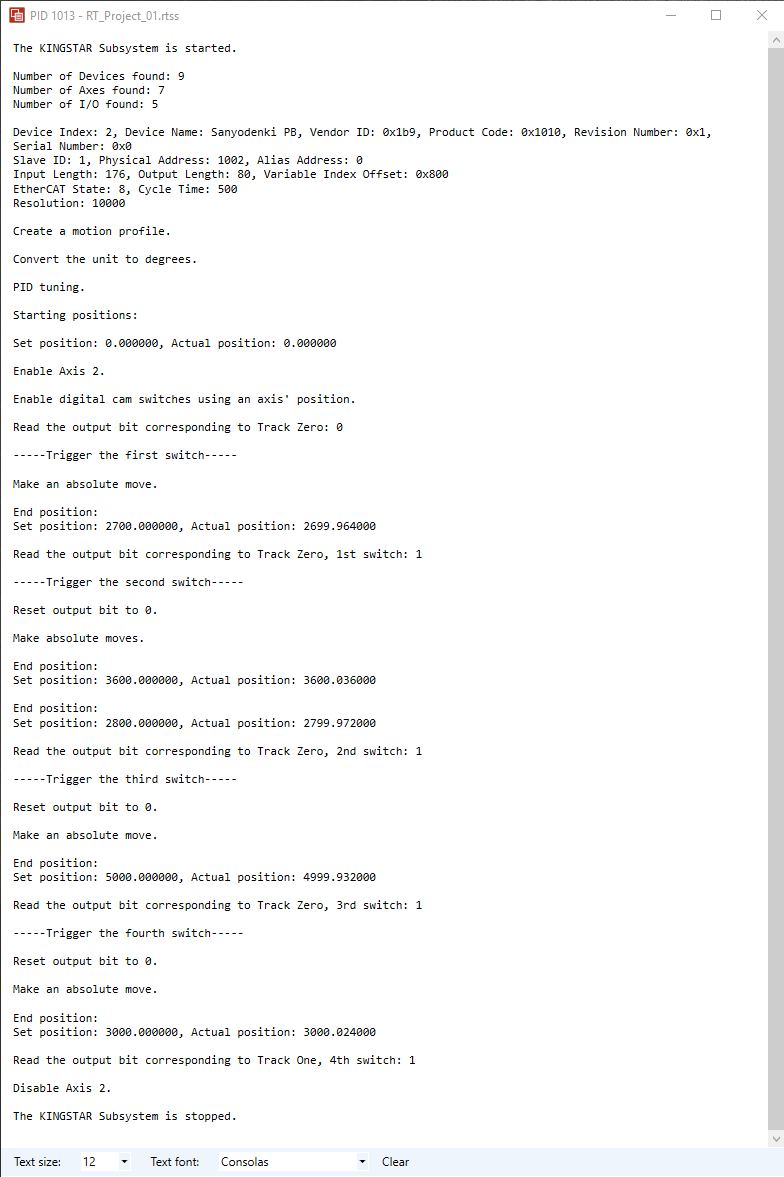
Main function
In this section, you'll learn how to apply all the code in this chapter to main.cpp. If everything is done correctly, you should be able to use an axis' position to control digital cam switches. To help you review what you have learned, we add comments into the code to describe the meaning of the functions.
- In
main.cpp, underTouchProbe.h, add the following code. - In
int _tmain, under the code blockif (!StartKingstar()), add the following code to get the number of devices on your EtherCAT network. - Under
RtPrintf("\n");, add the code depending on what switches you want to use. - If you want to trigger digital cam switches and digital cyclic switches, add the following code:
- If you want to trigger digital group cam switches, add the following code. You'll find that most code are the same as that in Chapter 10's Main function, because digital group cam switches need a group to work.
#include "DigitalSwitch.h" //Create an instance of the SubsystemStatus structure and get the state from it.
SubsystemStatus Subsystem = { ecatOffline, ecatOffline, 0, 0, 0, {ecatOffline}, {ecatOffline}, {axisOffline} };
GetStatus(&Subsystem, NULL);
//Display the details of the EtherCAT network.
RtPrintf("Number of Devices found: %d\n", Subsystem.SlaveCount);
RtPrintf("Number of Axes found: %d\n", Subsystem.AxesCount);
RtPrintf("Number of I/O found: %d\n", Subsystem.IOCount);
RtPrintf("\n");
int Axis = 2;
//Display the information of devices.
PrintDeviceInformation(Axis);
//Set a motion profile.
//You need to set a motion profile, or the minimum following error will be large.
MotionProfile(Axis);
//Convert the unit. In this tutorial we convert it to degrees.
PositionUnitConversion(Axis);
//PID tuning.
/*When you use velocity or torque modes, you must tune PID.
In this tutorial we use modeMasterIntPos, which doesn't require PID,
but you should offer PID values for your drive to get the best performance.*/
UpdatePID(Axis);
//Set the starting positions for an axis.
RtPrintf("Starting positions:\n\n");
SetAxisStartingPosition(Axis);
//Enable an axis.
EnableAxis(Axis);
//Enable digital switches using an axis' position.
DigitalCamSwitch(Axis);
//DigitalCyclicSwitch(Axis);
//Disable an axis.
DisableAxis(Axis);
//Stop the KINGSTAR Subsystem.
if (!StopKingstar())
{
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is not stopped.\n");
return -1;
}
else
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is stopped.\n");
return 0;
}
const int ARRLENGTH = 3;
int Axis[ARRLENGTH] = { 1, 5, 7 };
//Display the information of devices.
PrintDeviceInformation(Axis[0]);
PrintDeviceInformation(Axis[1]);
PrintDeviceInformation(Axis[2]);
//Set motion profiles.
//You need to set motion profiles, or the minimum following error will be large.
MotionProfile(Axis[0]);
MotionProfile(Axis[1]);
MotionProfile(Axis[2]);
//Set a group motion profile.
//It is optional to use a group motion profile.
MotionProfileGroup(0);
//Convert the unit. In this tutorial we convert it to degrees.
PositionUnitConversion(Axis[0]);
PositionUnitConversion(Axis[1]);
PositionUnitConversion(Axis[2]);
//PID tuning.
/*When you use velocity or torque modes, you must tune PID.
In this tutorial we use modeMasterIntPos, which doesn't require PID,
but you should offer PID values for your drive to get the best performance.*/
UpdatePID(Axis[0]);
UpdatePID(Axis[1]);
UpdatePID(Axis[2]);
//Add axes to Group Zero.
AssignAxis(0, Axis[0], 0);
AssignAxis(0, Axis[1], 1);
AssignAxis(0, Axis[2], 2);
//Set the starting positions for axes.
//SetGroupPositionOffset must be used when groups are disabled.
RtPrintf("Starting positions:\n\n");
SetGroupStartingPosition(0);
//Display a group's state.
GetAGroupState(0);
//Enable a group.
GroupEnable(0);
//Display a group's state.
GetAGroupState(0);
//Reset and enable axes.
EnableAxis(Axis[0]);
EnableAxis(Axis[1]);
EnableAxis(Axis[2]);
//Enable digital switches using a group's distance.
/*The code of this function is in DigitalSwitch.cpp. Since it needs
a group to run, it is put in Chapter 10's Main function.
To learn how it works, see Chapter 12.*/
GroupCamSwitch(0);
/* Stop a group */
//GroupHalt(0);
//GroupStop(0);
//Disable Group Zero.
GroupDisable(0);
//Remove all the axes in Group Zero at once.
RemoveGroup(0);
//Disable axes.
DisableAxis(Axis[0]);
DisableAxis(Axis[1]);
DisableAxis(Axis[2]);Complete code
In conclusion, to use digital cam switches and digital cyclic switches, in Chapter 12's main.cpp, your code should be as follows:
#include "RT_Project_01.h"
#include "SystemInitialization.h"
#include "IOModule.h"
#include "AxisConfiguration.h"
#include "SingleAxisMotion.h"
#include "Homing.h"
#include "Cam.h"
#include "Gear.h"
#include "GroupConfiguration.h"
#include "GroupMotion.h"
#include "TouchProbe.h"
#include "DigitalSwitch.h"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR * argv[])
{
//Start the KINGSTAR Subsystem.
if (!StartKingstar())
{
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is not started.\n");
return -1;
}
else
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is started.\n");
RtPrintf("\n");
//Create an instance of the SubsystemStatus structure and get the state from it.
SubsystemStatus Subsystem = { ecatOffline, ecatOffline, 0, 0, 0, {ecatOffline}, {ecatOffline}, {axisOffline} };
GetStatus(&Subsystem, NULL);
//Display the details of the EtherCAT network.
RtPrintf("Number of Devices found: %d\n", Subsystem.SlaveCount);
RtPrintf("Number of Axes found: %d\n", Subsystem.AxesCount);
RtPrintf("Number of I/O found: %d\n", Subsystem.IOCount);
RtPrintf("\n");
int Axis = 2;
//Display the information of devices.
PrintDeviceInformation(Axis);
//Set a motion profile.
//You need to set a motion profile, or the minimum following error will be large.
MotionProfile(Axis);
//Convert the unit. In this tutorial we convert it to degrees.
PositionUnitConversion(Axis);
//PID tuning.
/*When you use velocity or torque modes, you must tune PID.
In this tutorial we use modeMasterIntPos, which doesn't require PID,
but you should offer PID values for your drive to get the best performance.*/
UpdatePID(Axis);
//Set the starting positions for an axis.
RtPrintf("Starting positions:\n\n");
SetAxisStartingPosition(Axis);
//Enable an axis.
EnableAxis(Axis);
//Enable digital cam switches using an axis' position.
DigitalCamSwitch(Axis);
//Disable an axis.
DisableAxis(Axis);
//Stop the KINGSTAR Subsystem.
if (!StopKingstar())
{
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is not stopped.\n");
return -1;
}
else
RtPrintf("The KINGSTAR Subsystem is stopped.\n");
return 0;
}
To use digital group cam switches, in Chapter 10's main.cpp, your code should be as follows:
/* Chapter 10: Group Motion */
const int ARRLENGTH = 3;
int Axis[ARRLENGTH] = { 1, 5, 7 };
//Display the information of devices.
PrintDeviceInformation(Axis[0]);
PrintDeviceInformation(Axis[1]);
PrintDeviceInformation(Axis[2]);
//Set motion profiles.
//You need to set motion profiles, or the minimum following error will be large.
MotionProfile(Axis[0]);
MotionProfile(Axis[1]);
MotionProfile(Axis[2]);
//Set a group motion profile.
//It is optional to use a group motion profile.
MotionProfileGroup(0);
//Convert the unit. In this tutorial we convert it to degrees.
PositionUnitConversion(Axis[0]);
PositionUnitConversion(Axis[1]);
PositionUnitConversion(Axis[2]);
//PID tuning.
/*When you use velocity or torque modes, you must tune PID.
In this tutorial we use modeMasterIntPos, which doesn't require PID,
but you should offer PID values for your drive to get the best performance.*/
UpdatePID(Axis[0]);
UpdatePID(Axis[1]);
UpdatePID(Axis[2]);
//Add axes to Group Zero.
AssignAxis(0, Axis[0], 0);
AssignAxis(0, Axis[1], 1);
AssignAxis(0, Axis[2], 2);
//Set the starting positions for axes.
//SetGroupPositionOffset must be used when groups are disabled.
RtPrintf("Starting positions:\n\n");
SetGroupStartingPosition(0);
//Display a group's state.
GetAGroupState(0);
//Enable a group.
GroupEnable(0);
//Display a group's state.
GetAGroupState(0);
//Reset and enable axes.
EnableAxis(Axis[0]);
EnableAxis(Axis[1]);
EnableAxis(Axis[2]);
//Move an axis group
/* Linear moves */
//MoveLinearAbsoluteGroup(0);
//MoveLinearRelativeGroup(0);
//MoveLinearAdditiveGroup(0);
/* Circular moves */
//MoveCircularAbsoluteGroup(0);
//MoveCircularRelativeGroup(0);
//MoveCircularAdditiveGroup(0);
/* Helical moves */
//MoveHelicalAbsoluteGroup(0);
//MoveHelicalRelativeGroup(0);
//MoveHelicalAdditiveGroup(0);
/* Test moves */
//GroupJog(0);
//GroupInch(0);
/* Blending sample */
//BlendSample(0);
//Enable digital switches using a group's distance.
/*The code of this function is in DigitalSwitch.cpp. Since it needs
a group to run, it is put in Chapter 10's Main function.
To learn how it works, see Chapter 12.*/
GroupCamSwitch(0);
/* Stop a group */
//GroupHalt(0);
//GroupStop(0);
//Disable Group Zero.
GroupDisable(0);
//Remove all the axes in Group Zero at once.
RemoveGroup(0);
//Disable axes.
DisableAxis(Axis[0]);
DisableAxis(Axis[1]);
DisableAxis(Axis[2]);NOTE: To let you easily understand how to move an axis, we leave only necessary code in the main function. You can add more code depending on your needs.
NOTE: You probably have noticed that several header files are not used because we didn't include their related functions in the main function. Feel free to comment out unused header files. In the tutorial, we preserve all the header files in case you want to use any of the functions you have learned.
Output: