Use an IO-Link, MDP, or CANopen device
With EtherCAT, it is possible to add subnetworks using other protocols. Not all of these protocols can be scanned so you may need to provide information on the attached devices through an API. KINGSTAR has dedicated ST functions for three types of subnetworks. These functions should be used before ksStart is set to TRUE, so we recommend calling them in a program organization unit (POU) attached to the Init task. The following is the syntax for these functions:
unsigned char KsConfigureIoLinkDevice(long Index, long Port, unsigned char Revision, unsigned char Spdu, unsigned short Control, long InputLength, long OutputLength);
unsigned char KsConfigureMdpDevice(long Index, long Id, long InputLength, long OutputLength, long CommandCount, KS_SDO_COMMAND* Commands);
unsigned char KsConfigureCanDevice(long SlaveId, long CanId, long RxPdoCount, KS_CAN_PDO* RxPdos, long TxPdoCount, KS_CAN_PDO* TxPdos, long CommandCount, KS_SDO_COMMAND* Commands);These ST functions are adapted from the AddModuleConfiguration function in the KINGSTAR C interface. The first two parameters in them are corresponding to SlaveId and ModuleId in AddModuleConfiguration.
Index, SlaveId: Index refers to the index of a slave array; while SlaveId refers to the position of the slave in the network. When EtherCAT is started, this index has the same value as the SlaveId, which corresponds to the position of the slave in the network. Please note that after EtherCAT is started in the Operational (Op) state, any addition or removal of slaves from the network will change the position of the slaves in the network (SlaveId). Nevertheless, the index of the slave will remain the same. Newly added devices will be added in the back of the slave array. For all slaves after the change, the index and SlaveId will no longer match. This behavior is only available for physical devices; simulated devices are inapplicable. Please refer to the use cases in EnableHotConnect for more details.
Port, Id, CanId: module (devices linked to the coupler) ID. It can be slot ID, port ID, or CANopen slave ID.
The description of other parameters can be found in the IOLINK_SETTING, ECMDP_SETTING, and CANOPEN_SETTING structures.
To use these functions:
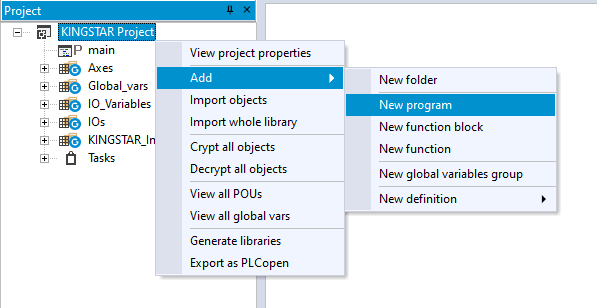
- In the Project panel, right-click KINGSTAR Project (your project name) and select Add > New program.
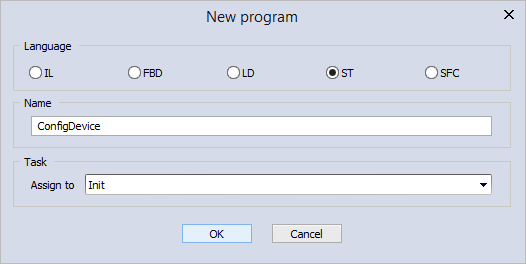
- In the New program dialog box, under Language, select ST. In the Name box, enter your program name. We enter "ConfigDevice." Under Task, in the Assign to list, select Init. When you finish editing, click OK.
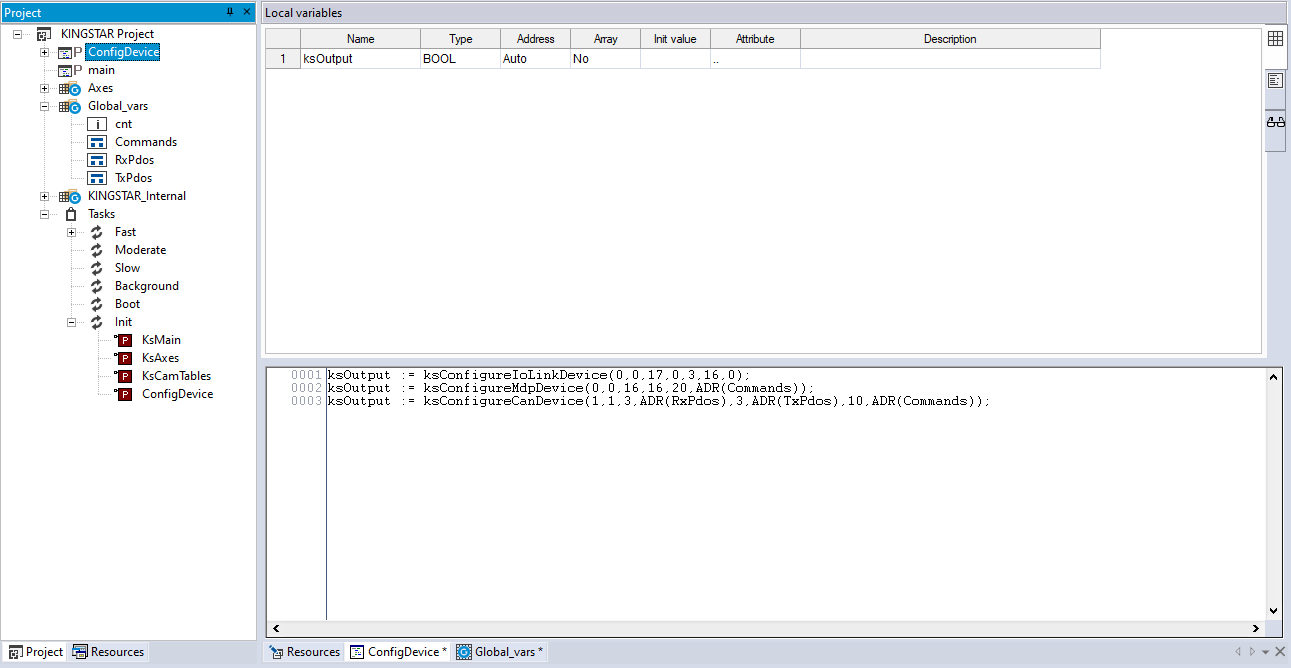
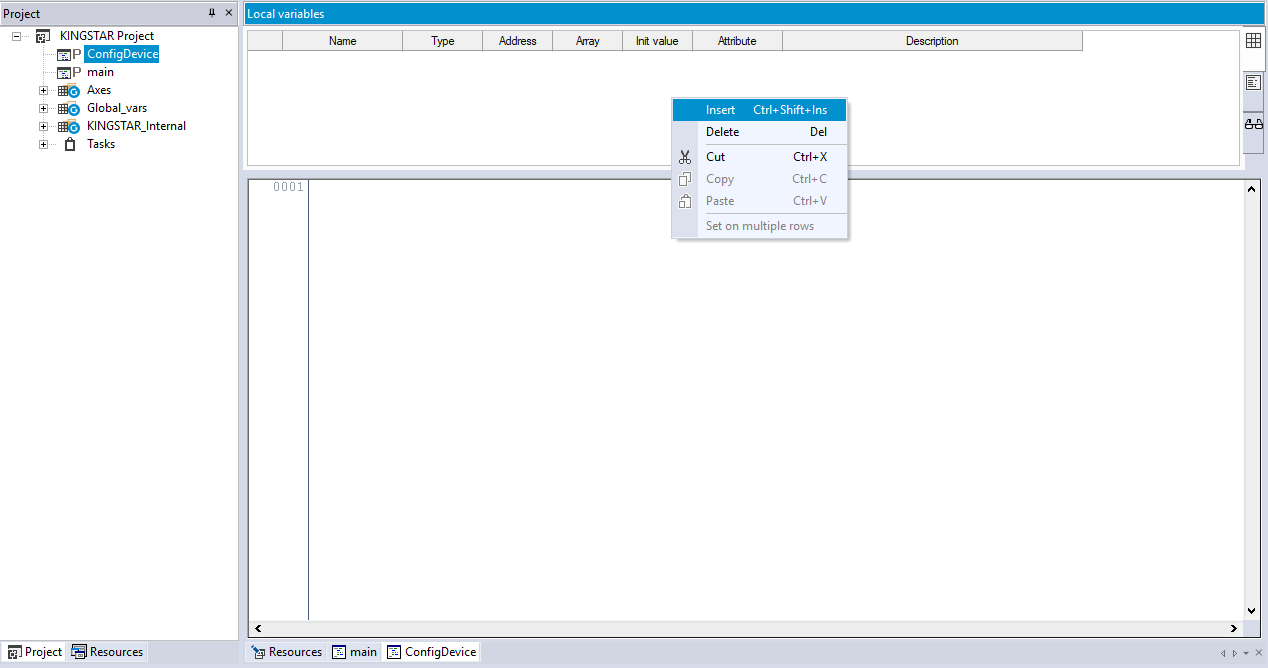
- In the ConfigDevice panel, in the Local variables editor, right-click an empty area and select Insert.
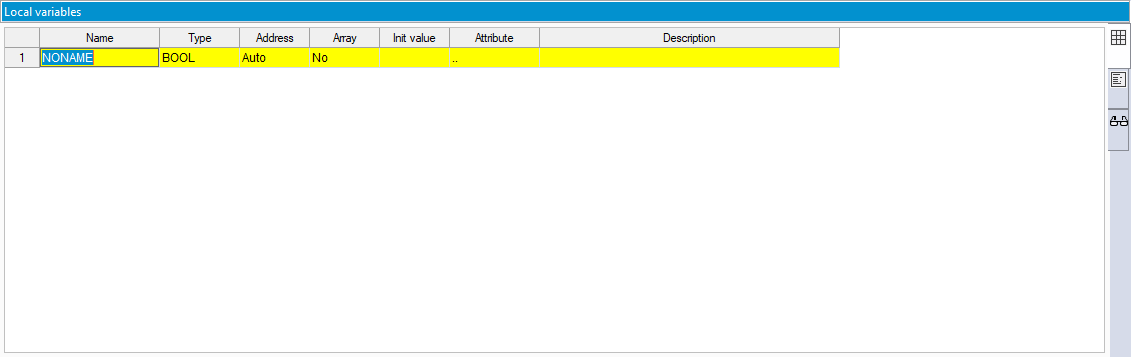
- A local variable is created. Click its Name cell.
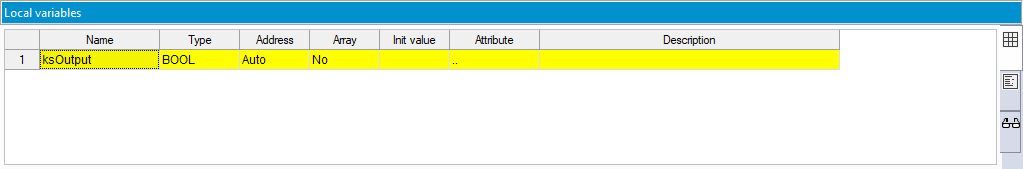
- Enter a meaningful name for the variable and press Enter. In this guide, we enter the name "ksOutput."
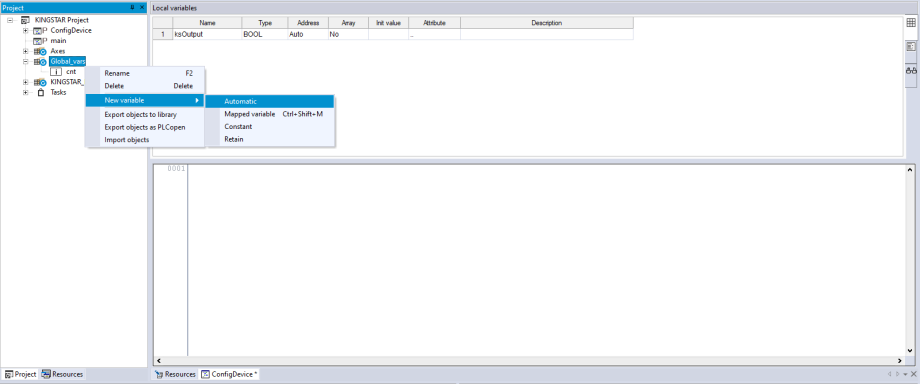
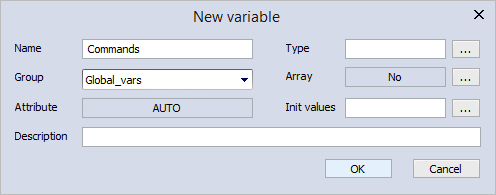
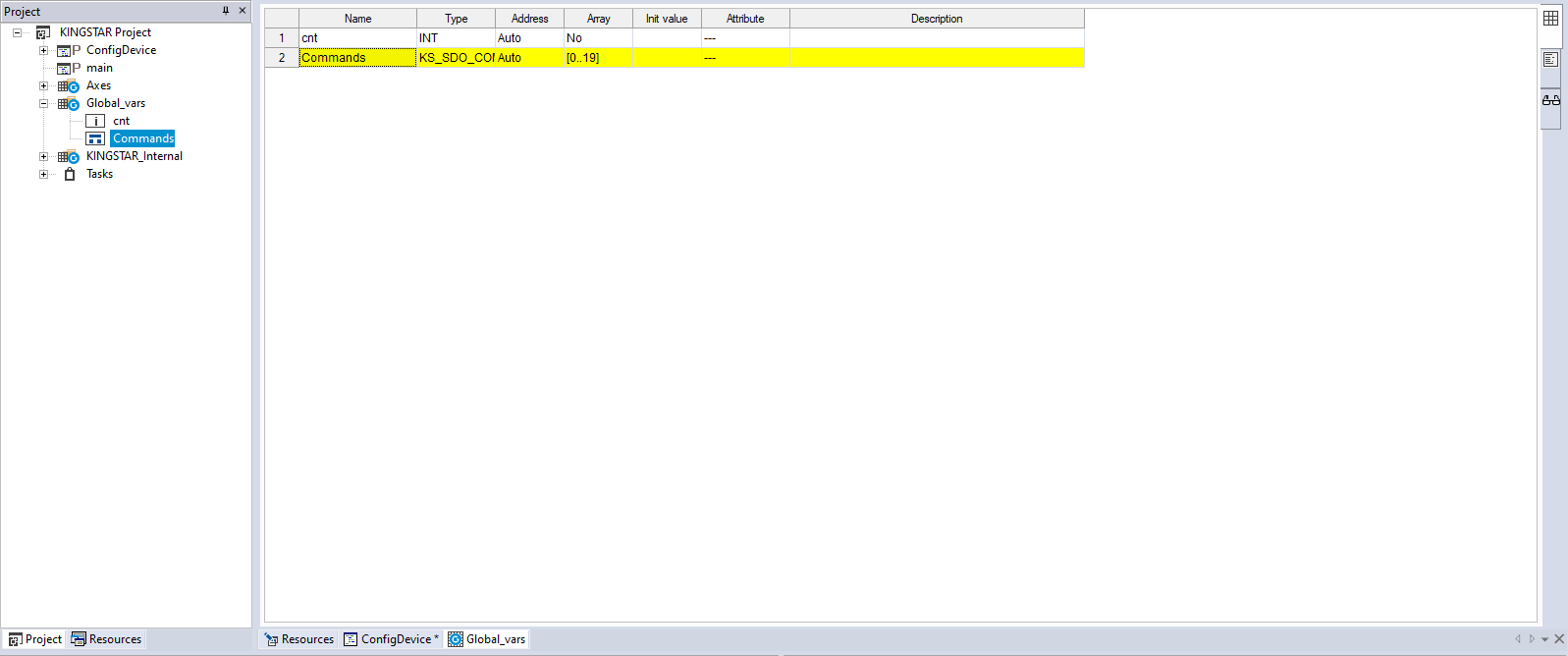
- In the Project panel, right-click Global_vars (your group name) and select New variable > Automatic to add a global variable.
- In the New variable dialog box, in the Name box, enter "Commands." In the Type box, click ... to open Object browser.
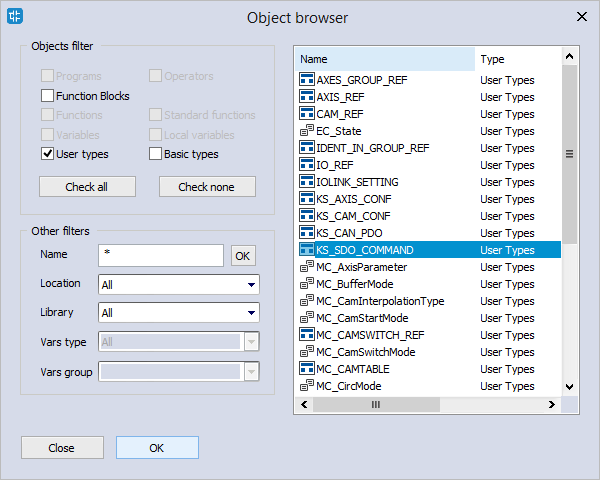
- In Object browser, in which select the User types check box. In the User types list, select KS_SDO_COMMAND, and click OK.
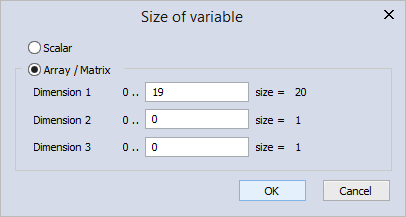
- In the New variable dialog box, in the Array box, click ... to open Size of variable, in which select Array / Matrix. In the Dimension 1 box, enter "19," so the array size is 20. You can define your own array size. After you finish editing, click OK.
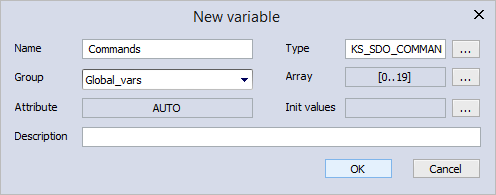
- In the New variable dialog box, click OK.
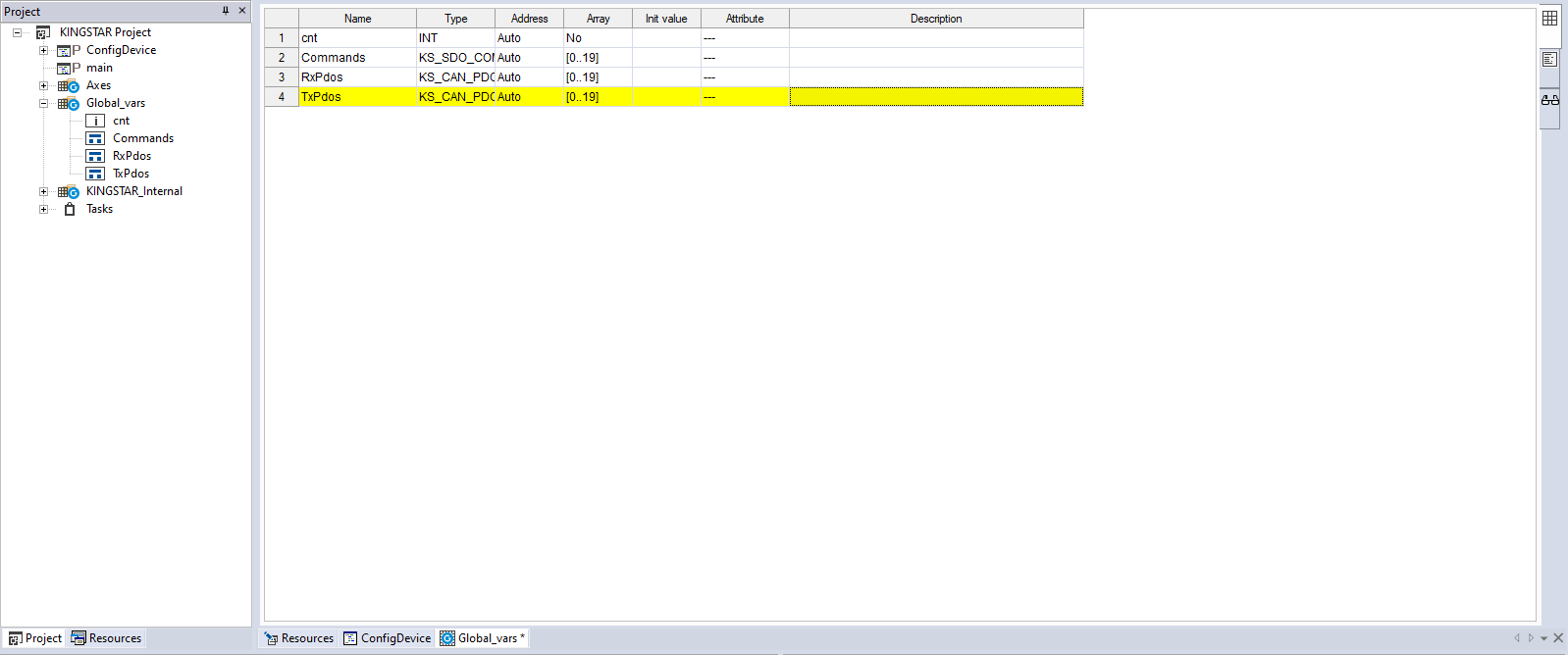
- In the Project panel, in the Global_vars group, the Commands variable has been added. Double-click Commands to open the Global_vars panel.
- In the Global_vars panel, add other two variables called RxPdos and TxPdos. Their types are KS_CAN_PDO and array sizes are 20.
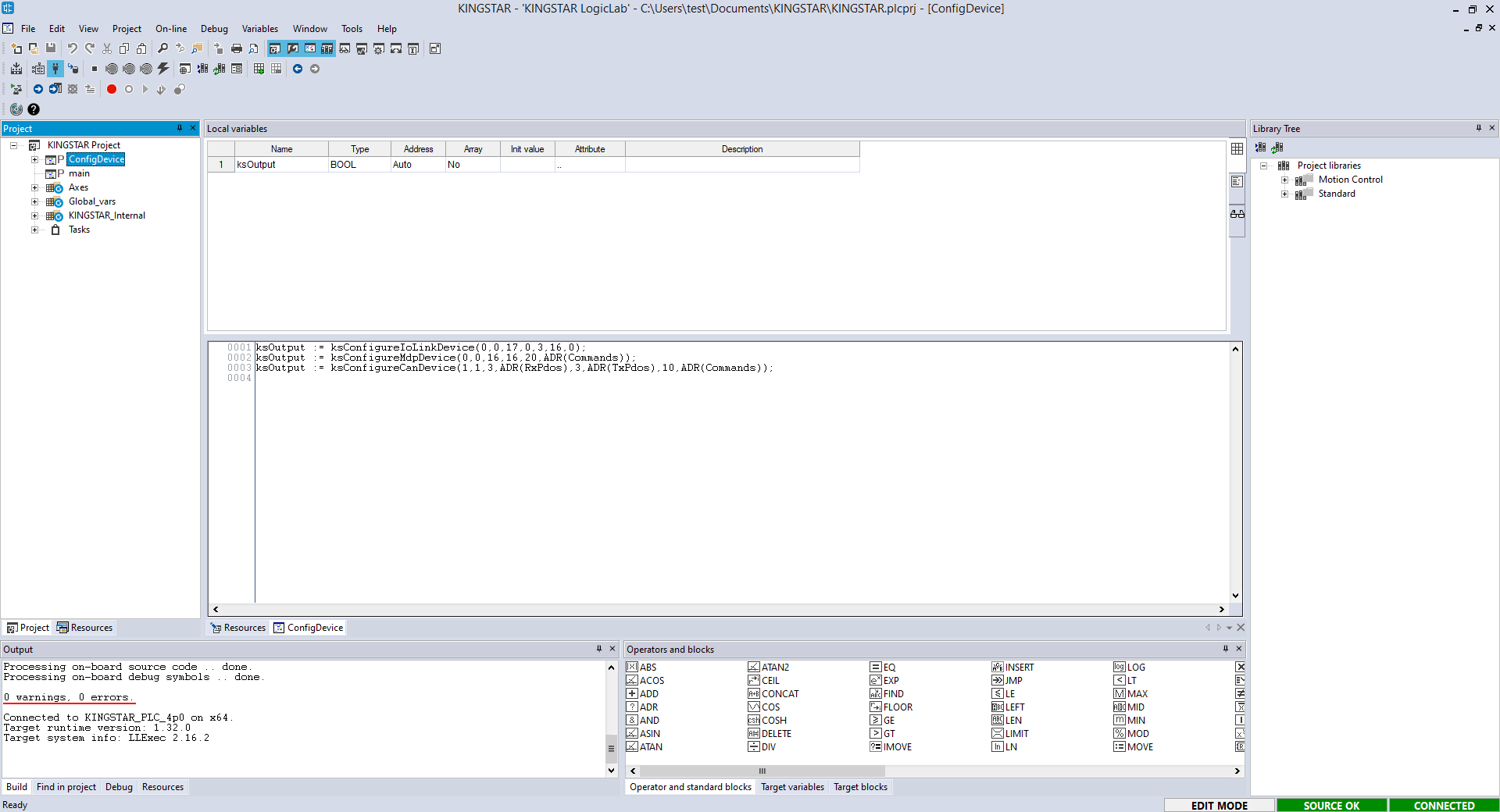
- In the Project panel, double-click ConfigDevice. In the source code editor, enter your code. The following is the sample code. You should choose the function that meets your needs, and modify your code depending on your device and its settings.
- Compile and run your program.
ksOutput := ksConfigureIoLinkDevice(0,0,17,0,3,16,0);
ksOutput := ksConfigureMdpDevice(0,0,16,16,20,ADR(Commands));
ksOutput := ksConfigureCanDevice(1,1,3,ADR(RxPdos),3,ADR(TxPdos),10,ADR(Commands));