| Function block | MC_GearInPos | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
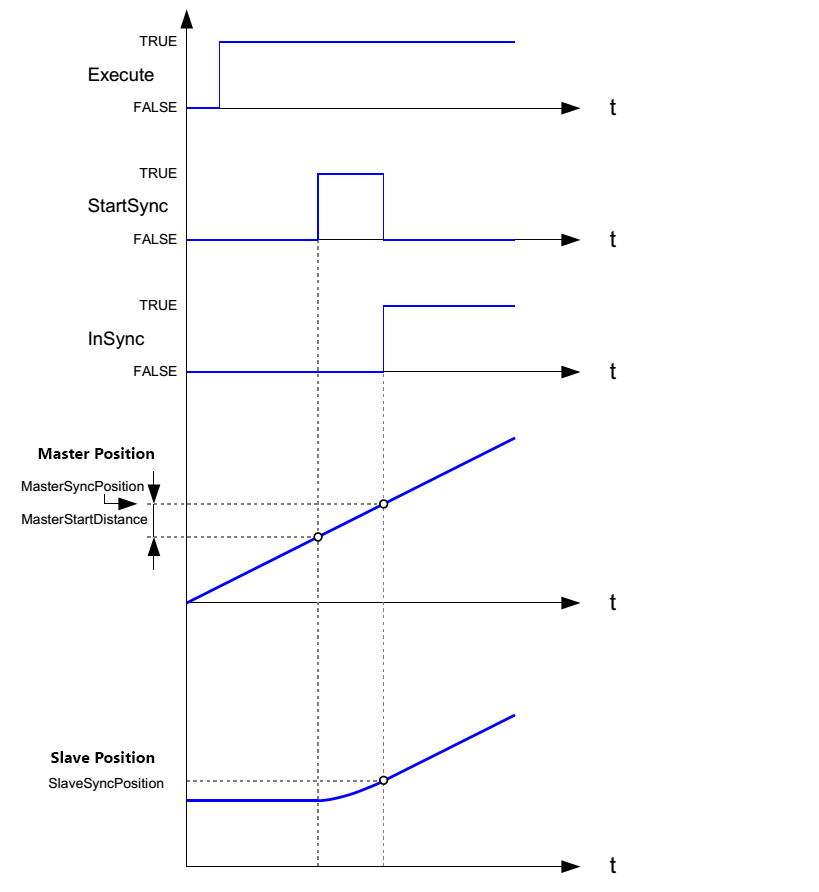
Commands a gear ratio between the position of the slave and master axes from the synchronization point onwards. How it works: First, the slave axis does an MC_MoveContinuousAbsolute move to reach the SlaveSyncPosition at the right time with the right velocity. The Velocity, Acceleration, and Deceleration inputs are for this MC_MoveContinuousAbsolute move. While this move is running, the StartSync output is TRUE. Once this motion is done, the InSync output is TRUE. GearInPos profiles:
|
|||
| VAR_IN_OUT | |||
| B | MasterIn | AXIS_REF | Reference to the master axis. |
| B | SlaveIn | AXIS_REF | Reference to the slave axis. The number of slaves is up to 32. |
| VAR_INPUT | |||
| B | Execute | BOOL | Starts gearing at the rising edge. |
| V | Permanent | BOOL |
Determines whether the gear state is preserved after the motor is disabled. TRUE: The gear state is preserved even if the motor is disabled. For example, if the master axis is enabled, the slave axis will be enabled. If an error has occurred on the master, it occurred on the slave too. FALSE: The gear state won't be preserved after the motor is disabled. |
| B | RatioNumerator | INT | Gear ratio numerator. |
| B | RatioDenominator | UINT | Gear ratio denominator. |
| E | MasterValueSource | MC_Source |
Defines the source for synchronization:
NOTE: mcSecondEncoderValue is not supported yet. |
| B | MasterSyncPosition | LREAL |
The master's position where the slave is in sync with the master. |
| B | SlaveSyncPosition | LREAL | The slave's position where the slave is in sync with the master. |
| E | SyncMode | MC_SyncMode | Defines the way to synchronize. |
| E | MasterStartDistance | LREAL | The distance for the master to travel to synchronize with the slave (when the slave axis is started to get into synchronization). |
| E | Velocity | LREAL | Maximum velocity during the time difference between StartSync and InSync. |
| E | Acceleration | LREAL | Maximum acceleration during the time difference StartSync and InSync. |
| E | Deceleration | LREAL | Maximum deceleration during the time difference StartSync and InSync. |
| E | Jerk | LREAL | Maximum jerk during the time difference StartSync and InSync. |
| E | BufferMode | MC_BufferMode | Defines how to blend the velocity of two function blocks. |
| VAR_OUTPUT | |||
| E | StartSync | BOOL | Commanded gearing starts. |
| B | InSync | BOOL | The synchronization state of the axis. TRUE: The synchronization is completed. FALSE: The slave axis is synchronizing with the master axis. |
| E | Busy | BOOL | The function block is not finished and new output values are to be expected. |
| E | Active | BOOL | The function block is controlling the axis. |
| E | CommandAborted | BOOL | The command is aborted by another command. |
| B | Error | BOOL | Signals that an error has occurred within the function block. |
| E | ErrorID | MC_Error | Error identification. |
|
|||
| MC_GearInPos | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AXIS_REF | MasterIn | Master | AXIS_REF | |||
| AXIS_REF | SlaveIn | Slave | AXIS_REF | |||
| BOOL | Execute | StartSync | BOOL | |||
| BOOL | Permanent | InSync | BOOL | |||
| INT | RatioNumerator | Busy | BOOL | |||
| UINT | RatioDenominator | Active | BOOL | |||
| MC_Source | MasterValueSource | CommandAborted | BOOL | |||
| LREAL | MasterSyncPosition | Error | BOOL | |||
| LREAL | SlaveSyncPosition | ErrorID | MC_Error | |||
| MC_SyncMode | SyncMode | |||||
| LREAL | MasterStartDistance | |||||
| LREAL | Velocity | |||||
| LREAL | Acceleration | |||||
| LREAL | Deceleration | |||||
| LREAL | Jerk | |||||
| MC_BufferMode | BufferMode | |||||
Timing Diagram of MC_GearInPos