Control modes
The KINGSTAR Subsystem offers several control modes for controlling your motor drives under EtherCAT fieldbus. These control modes are designed based on the Profile Position (PP), Cyclic Synchronous Position (CSP), Cyclic Synchronous Velocity (CSV) and Cyclic Synchronous Torque (CST) modes of operation specified in CiA 402. After selecting a control mode, you can issue the related commands to control the motor drives.
Typically, motor drives offer three basic operation modes, which include position, velocity, and torque. Each of these operation modes can be further utilized for motion control planning through direct commands, PID parameter configuration and interpolation. The table below shows the correlation between the KINGSTAR control modes and the CiA 402 modes of operation.
| Basic Modes | Methods | KINGSTAR Control Modes | Calculations Done by KINGSTAR | CiA 402 Modes of Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Slave interpolation |
(not supported yet) |
- | Profile Position (PP) |
| Direct command | modeDirectPos | - | Cyclic Synchronous Position (CSP) | |
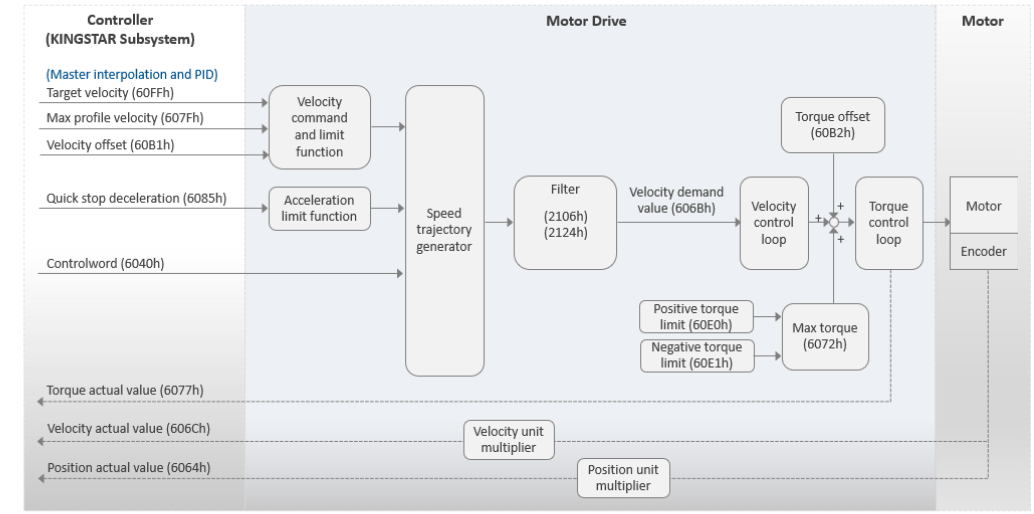
| Master interpolation | modeMasterIntPos | Interpolation | ||
| Velocity | Direct command | modeDirectVel | - | Cyclic Synchronous Velocity (CSV) |
| PID | modePidVel | PID (Position control loop) | ||
| Master interpolation | modeMasterIntVel |
Interpolation PID (Position control loop) |
||
| Torque | Direct command | modeDirectTor | - | Cyclic Synchronous Torque (CST) |
| PID | modePidTor | PID (Position control loop and Velocity control loop) | ||
| Master interpolation | modeMasterIntTor |
Interpolation PID (Position control loop and Velocity control loop) |
||
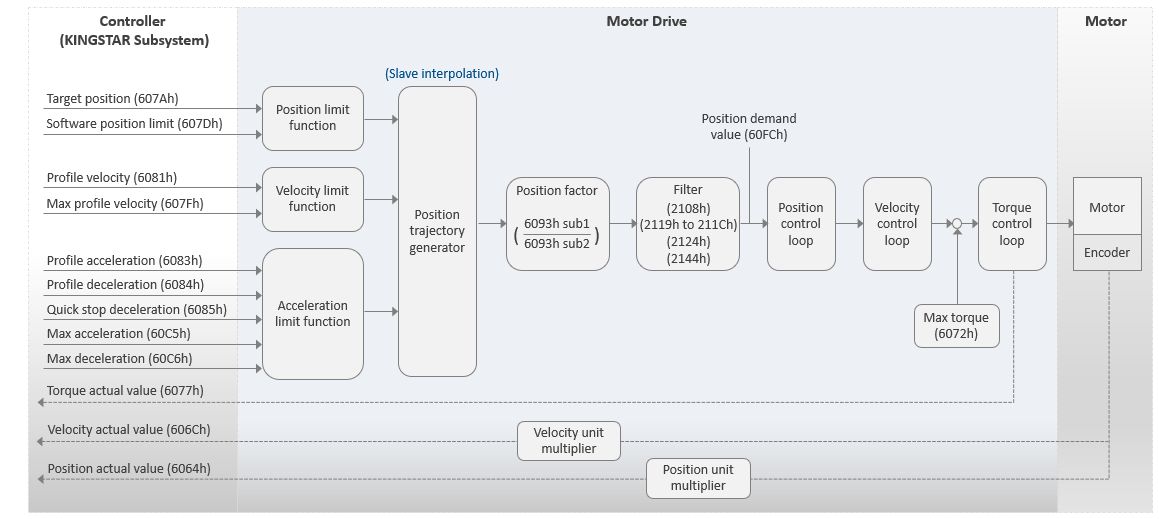
modeSlaveInt
This mode is not supported yet.
This mode is called Slave Interpolation mode. The motor drive operates in Profile Position (PP) mode. In this mode, most calculations are done in the motor drive, such as interpolation and PID. The controller only informs the motor drive of the target position and motion profiles. The trajectory generator in the motor drive will perform the interpolation.
Basic process flow:
- The KS sends the target position (607Ah) and motion profiles to the motor drive.
- The motor drive performs the interpolation for each cycle based on the target position and motion profiles.
- The motor drive uses its PID algorithm to first convert the position into velocity and then further converts the velocity into torque. Finally, the motor drive converts the torque into current for the motor.
- KS receives the actual position from the motor drive.
- The steps 2-4 are repeated until the motor reaches its destination. The motor drive then signals the KS that the movement has ended.
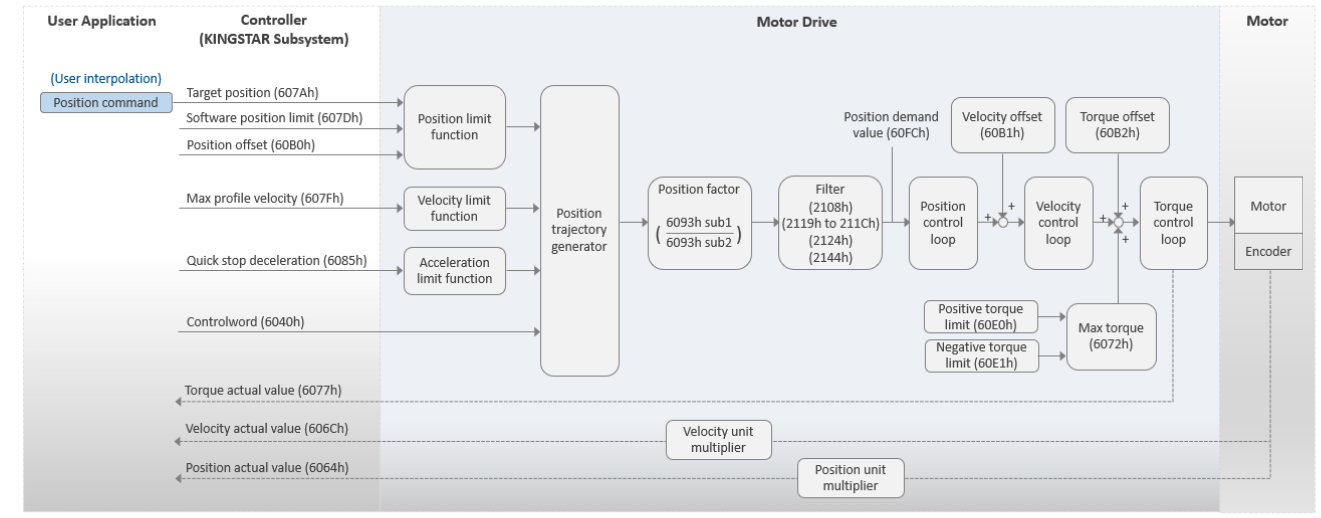
modeDirectPos
This mode is called Direct Position mode. The motor drive operates in Cyclic Synchronous Position (CSP). In this mode, your application needs to perform the interpolation and send a position command to the KINGSTAR Subsystem (KS) every EtherCAT cycle. The KS will send the target position and motion profiles to the motor drive. The motor drive will use its PID to fine-tune the parameters. You can use the velocity offset and torque offset as the velocity and torque feed forward control setting. MoveAxis cannot be used under this mode.
NOTE: We suggest you use this mode only for RT API.
Basic process flow:
- Your application performs the interpolation and then passes the position command to the KS using SetAxisPosition.
- The KS sends the target position (607Ah) and motion profiles to the motor drive.
- The motor drive uses its PID algorithm to first convert the position into velocity and then further converts the velocity into torque. Finally, the motor drive converts the torque into current for the motor.
- KS receives the actual position from the motor drive.
- Users can repeat these steps to control the motor to reach a specific position.
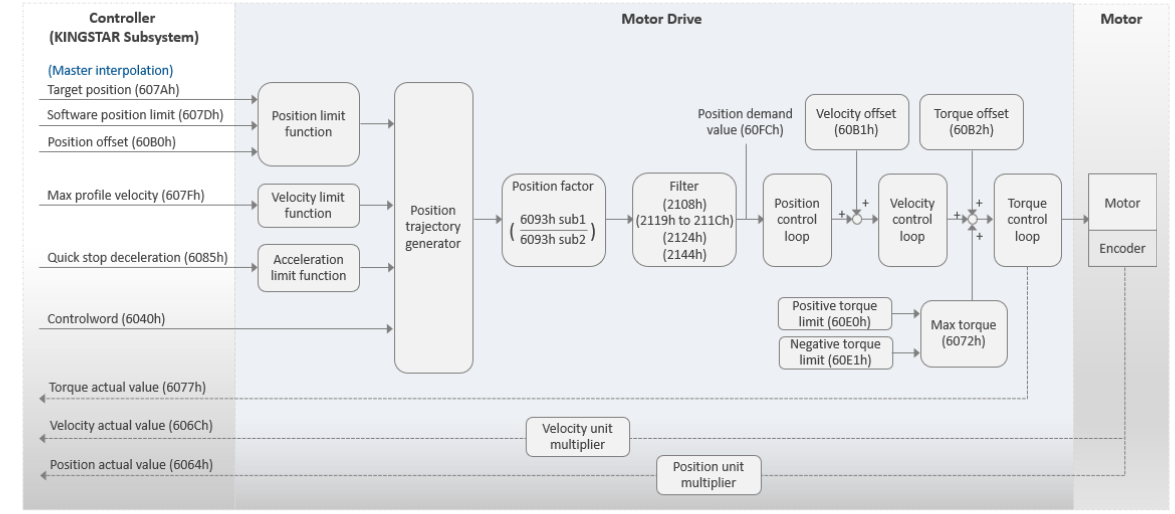
modeMasterIntPos
This mode is called Master Interpolation Position mode. The motor drive operates in Cyclic Synchronous Position (CSP). In this mode, the KINGSTAR Subsystem (KS) will handle the interpolation; while the drive will use its PID to fine-tune the parameters.
Basic process flow:
- You use various functions to command a movement to the KS.
- The KS performs the interpolation for each cycle based on the target position and motion profiles.
- The KS sends the target position (607Ah) to the motor drive.
- The motor drive uses its PID algorithm to first convert the position into velocity and then further converts the velocity into torque. Finally, the motor drive converts the torque into current for the motor.
- KS receives the actual position from the motor drive.
- The steps 2-5 are repeated until the motor reaches its destination.
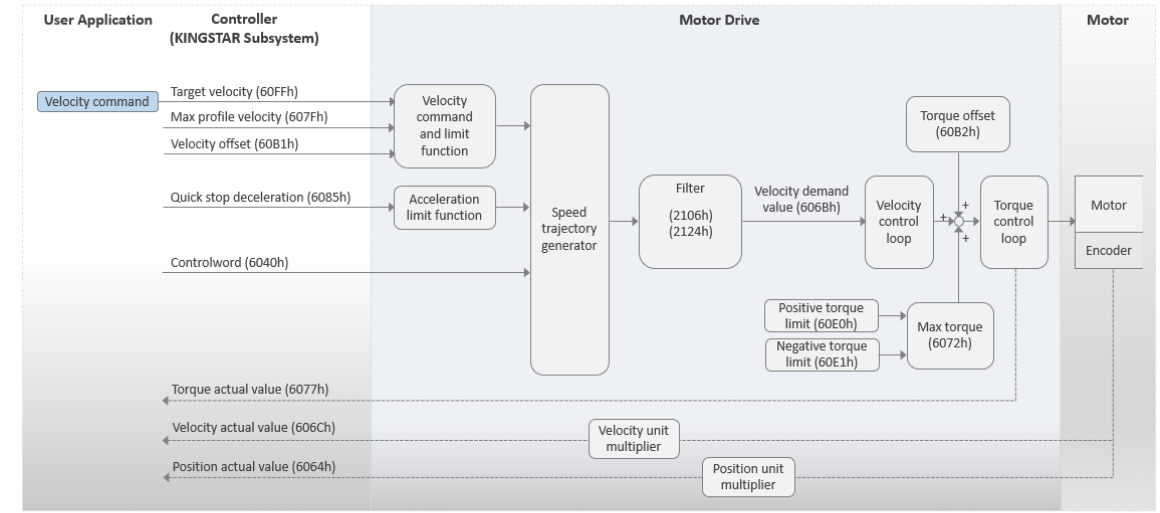
modeDirectVel
This mode is called Direct Velocity mode. The motor drive operates in Cyclic Synchronous Velocity (CSV). In this mode, your application needs to pass the velocity command to the KINGSTAR Subsystem (KS) every EtherCAT cycle. The KS will send the target velocity to the motor drive. You can use the torque offset as the torque feed forward control setting. MoveAxis cannot be used under this mode.
NOTE: We suggest you use this mode only for RT API.
Basic process flow:
- Your application passes the velocity command to the KS using SetAxisVelocity.
- The KS sends the target velocity (60FFh) to the motor drive. The velocity command is positively correlated with the target velocity (60FFh).
- The motor drive uses its PID algorithm to convert the velocity into torque, and then converts the torque into current for the motor.
- KS receives the actual velocity from the motor drive.
-
Users can repeat these steps to control the motor to move at a specific velocity.
modePidVel
This mode is called PID Velocity mode. The motor drive operates in Cyclic Synchronous Velocity (CSV). In this mode, your application needs to perform the interpolation. The KINGSTAR Subsystem (KS) will use its PID to convert the position into velocity and then send the target velocity to the motor drive. You can use the torque offset as the torque feed forward control setting. MoveAxis cannot be used under this mode.
Basic process flow:
- Your application performs the interpolation and then passes the position command to the KS using SetAxisPosition.
- The KS uses its PID to convert the position into velocity. Note that you will need to use the KS's APIs to configure the PID parameters. Please refer to Motion and PID in McAxisParameter.
- The KS sends the target velocity (60FFh) to the motor drive.
- The motor drive uses its PID algorithm to convert the velocity into torque, and then converts the torque into current for the motor.
- KS receives the actual velocity from the motor drive.
- These steps are repeated until the motor reaches its destination.
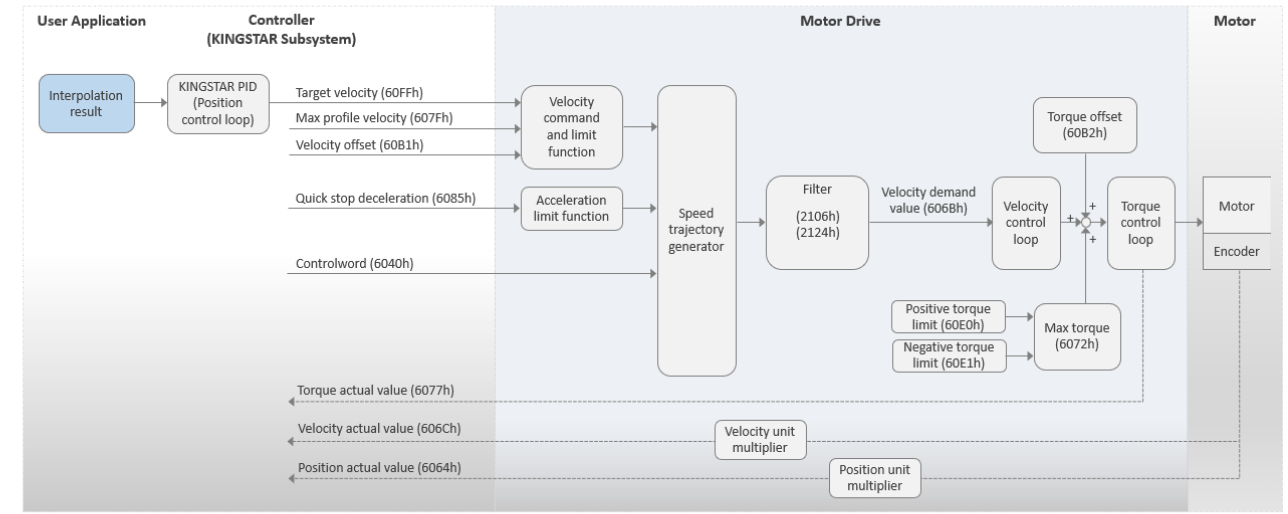
modeMasterIntVel
This mode is called Master Interpolation Velocity mode. The motor drive operates in Cyclic Synchronous Velocity (CSV). In this mode, the KINGSTAR Subsystem (KS) will handle the interpolation and use its PID to convert the position into velocity and then send the target velocity to the motor drive. You can use the torque offset as the torque feed forward control setting.
Basic process flow:
- You use various functions to command a movement to the KS.
- The KS performs the interpolation.
- The KS uses its PID to convert the position into velocity. Note that you will need to use the KS's APIs to configure the PID parameters. Please refer to Motion and PID in McAxisParameter.
- The KS sends the target velocity (60FFh) to the motor drive.
- The motor drive uses its PID algorithm to convert the velocity into torque, and then converts the torque into current for the motor.
- KS receives the actual velocity from the motor drive.
- The steps 2-6 are repeated until the motor reaches its destination.
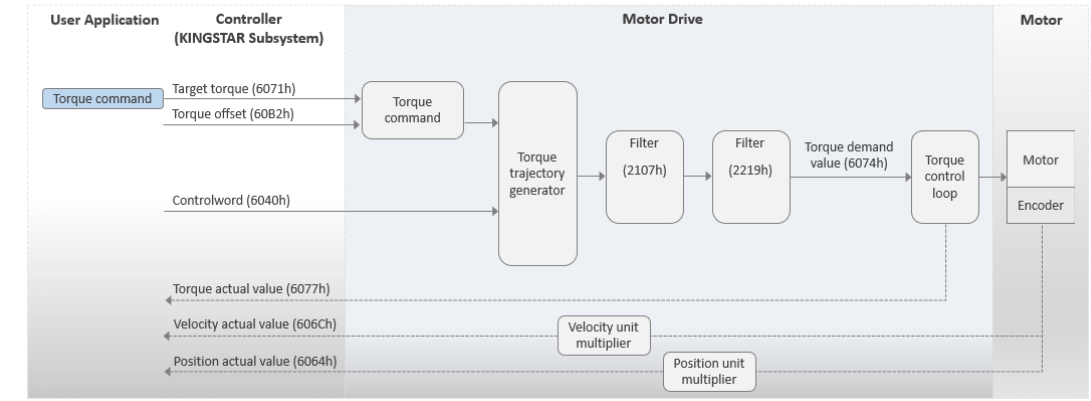
modeDirectTor
This mode is called Direct Torque mode. The motor drive operates in Cyclic Synchronous Torque (CST). In this mode, your application needs to pass the torque command to the KINGSTAR Subsystem (KS) every EtherCAT cycle. The KS will send the target torque to the motor drive. You can use the torque offset as the torque feed forward control setting. MoveAxis cannot be used under this mode.
NOTE: We suggest you use this mode only for RT API.
IMPORTANT: Torque doesn't have the default value. You must tune the torque and find the best PID parameters before you use this mode. You may use the Tune function in the KINGSTAR Configuration Tool, or use your own tool for tuning.
Basic process flow:
- Your application passes the torque command to the KS using SetAxisTorque.
- The KS sends the target torque (6071h) to the motor drive. The torque command is positively correlated with the target torque (6071h).
- The motor drive uses its PID algorithm to convert the torque into current for the motor.
- KS receives the actual torque.
-
Users can repeat these steps to control the motor to move at a specific torque.
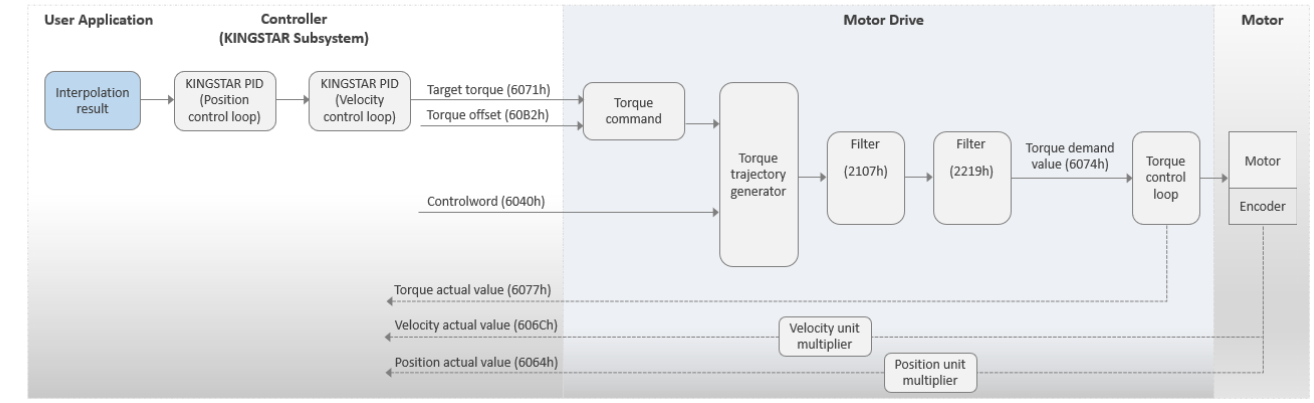
modePidTor
This mode is called PID Torque mode. The motor drive operates in Cyclic Synchronous Torque (CST). In this mode, your application needs to perform the interpolation. The KINGSTAR Subsystem (KS) will use its PID to convert the position into velocity and then convert the velocity into torque. Finally, the KS will send the target torque to the motor drive. You can use the torque offset as the torque feed forward control setting. MoveAxis cannot be used under this mode.
Basic process flow:
- Your application performs the interpolation and then passes the position command to the KS using SetAxisPosition.
- The KS uses its PID to convert the position into velocity and then convert the velocity into torque. Note that you will need to use the KS's APIs to configure the PID parameters. Please refer to Motion and PID in McAxisParameter.
- The KS sends the target torque (6071h) to the motor drive.
- The motor drive uses its PID algorithm to convert the torque into current for the motor.
- KS receives the actual torque.
- These steps are repeated until the motor reaches its destination.
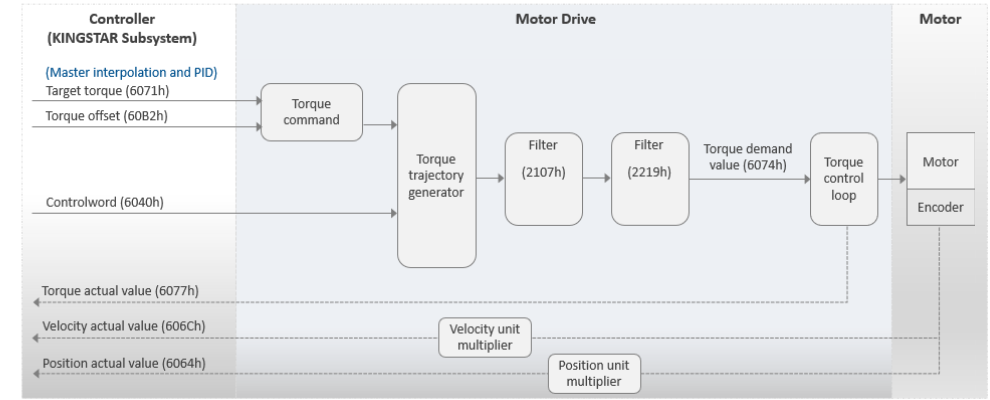
modeMasterIntTor
This mode is called Master Interpolation Torque mode. The motor drive operates in Cyclic Synchronous Torque (CST). In this mode, the KINGSTAR Subsystem (KS) will handle the interpolation and use its PID to convert the position into velocity and then convert the velocity into torque. Finally, the KS will send the target torque to the motor drive. You can use the torque offset as the torque feed forward control setting.
Basic process flow:
- You use various functions to command a movement to the KS.
- The KS performs the interpolation.
- The KS uses its PID to convert the position into velocity and then convert the velocity into torque. Note that you will need to use the KS's APIs to configure the PID parameters. Please refer to Motion and PID in McAxisParameter.
- The KS sends the target torque (6071h) to the motor drive.
- The motor drive uses its PID algorithm to convert the torque into current for the motor.
- KS receives the actual torque.
- The steps 2-6 are repeated until the motor reaches its destination.
Selecting a control mode
To choose a control mode, use the SetAxisControlMode (RT and Win32) or SetAxisControlMode (.NET API) function, or IAxis.ControlMode (.NET Class) property. The control mode must be compatible with the current access mode, which is set using the SetAxisAccessMode (RT and Win32) or SetAxisAccessMode (.NET API) function, or ISubsystem.Access (.NET Class) property before the connection is established. Not all drives support control mode changes while the motor is powered on.
See also
RT and Win32 – KINGSTAR Motion - Axis configuration
RT and Win32 – KINGSTAR Motion - Types
.NET API – Motion - Axis configuration
.NET Class – IAxis Interface - Properties
.NET Enumeration