Modbus TCP master
To use Modbus TCP master, we need to decide which TCP port sends data, and use this port to send a Modbus command to a TCP slave.
NOTE: Before you use TCP master, make sure you have already assigned a network interface card (NIC) to RTX64. For further details about how to assign an NIC, see Modbus TCP.
- In the Project pane, add a new program with FBD. You can decide its name and task, or use the settings we provided.
- In Library Tree, drag the following function blocks (FBs) to the source editor and give them meaningful names. TCP_Connect is the TCP port that the TCP master uses to send data. Mb_ReadCoils_10 is a command that reads a slave's Coil. You can use other commands if you want. After you add the FBs to the source editor, they will also be added to local variables.
- Connectivity > Ethernet > TCP_Connect
- Connectivity > Modbus > Mb_ReadCoils_10
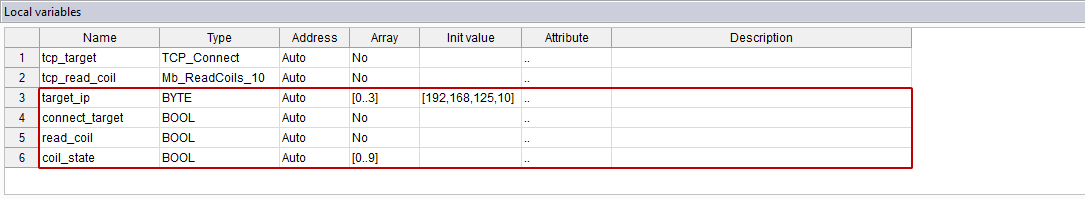
- Add the following variables. Two of them control the Enable and Execute state of TCP_Connect and Mb_ReadCoils_10, respectively. One of them stores the IP address of a TCP slave, and another displays the value the master reads.
- Add the following inputs and outputs to the FBs as the screen shot shows.
- Compile and run the PLC program. To toggle the BOOL variables, drag them to the Watch panel and set their values. Remember, you need to turn on the Enable and Execute states of the FBs so they can start working.
- Connect your computer to an I/O module using an Ethernet cable.
- Assign an NIC to RTX64 for Modbus.
- Add
connect_target,read_coil,tcp_target,tcp_read_coil, andcoil_stateto the Watch panel. Useconnect_targetandread_coilto enable the two FBs and check their Enable and Execute states. They will be TRUE if the FBs are enabled successfully. - After both FBs start to run,
coil_stategets the value from the I/O module it reads. In this guide, we read the address 1282. When you read your I/O module's data, you should check the address range of your I/O module and enter the address you want to read.
Language: FBD
Name: mb_tcp_master
Task: Fast
NOTE: For more information about how to add a new program, see PLC programming.


| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | Variable 3 | Variable 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attributes |
Name: target_ip Type: BYTE Address: Auto Array: 0..3 Init value: 192, 168, 125, 10 |
Name: connect_target Type: BOOL Address: Auto |
Name: read_coil Type: BOOL Address: Auto |
Name: coil_state Type: BOOL Address: Auto Array: 0..9 |
| Usage | Store the IP address of a TCP slave. | Enable or disable TCP_Connect. | Enable or disable Mb_ReadCoils_10. | Display the value read. |
NOTE: To know the range of Coils, Discrete Inputs, Holding Registers, and Input Registers, in Library Tree, expand ModbusSlaveData, double click an item.

If you want to use the TCP master example in this guide to test Modbus TCP data transmission, do the following:
NOTE: For more information about compiling and running, see Compile and run your PLC program.
NOTE: For more information about toggling a boolean, see Step 8 in Start and stop the KINGSTAR Subsystem through variables.
