| Function block | MC_GroupStop | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Commands a controlled motion stop and transfers the axis group to the state GroupStopping. It aborts any ongoing function block execution. While the axis group is in the GroupStopping state, no other function block can perform any motion on the same axis group. After the axis group has reached velocity zero, the Done output is set to TRUE immediately. The axis group remains in the GroupStopping state as long as Execute is TRUE or velocity zero is not yet reached. As soon as Done is TRUE and Execute is FALSE, the axis group goes to the GroupStandBy state. The command can only be aborted by MC_GroupDisable. | |||
| VAR_IN_OUT | |||
| B | GroupIn | AXES_GROUP_REF | Reference to a group of axes. References are zero based. You can have up to 32 groups. |
| VAR_INPUT | |||
| B | Execute | BOOL | Starts the action at rising edge. |
| E | Deceleration | LREAL | Value of the deceleration. The unit is determined by MC_ProfileType. [unit/second2] or [second] |
| E | Jerk | LREAL | Value of the jerk. The unit is determined by MC_ProfileType. [unit/second3] or [second] |
| VAR_OUTPUT | |||
| B | Done | BOOL | All axes has stopped. |
| E | Busy | BOOL | The function block is not finished. |
| E | CommandAborted | BOOL | Command is aborted using MC_Power to disable one or more of the axes in the group. The state changes to GroupDisabled. |
| B | Error | BOOL | Signals that an error has occurred within the function block. |
| E | ErrorID | MC_Error | Error identification. |
|
|||
| MC_GroupStop | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AXES_GROUP_REF | GroupIn | Group | AXES_GROUP_REF | |||
| BOOL | Execute | Done | BOOL | |||
| LREAL | Deceleration | Busy | BOOL | |||
| LREAL | Jerk | CommandAborted | BOOL | |||
| Error | BOOL | |||||
| ErrorID | MC_Error | |||||
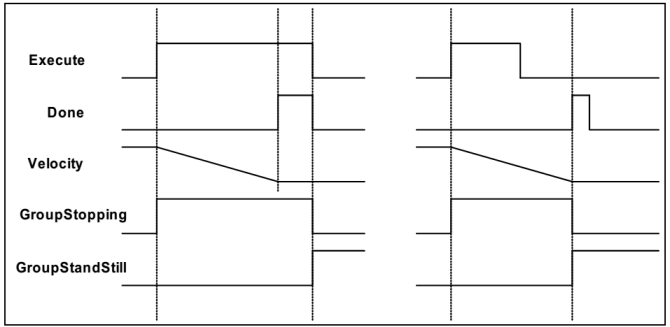
A typical timing diagram for MC_GroupStop is shown below, including the relevant states and state-transitions.
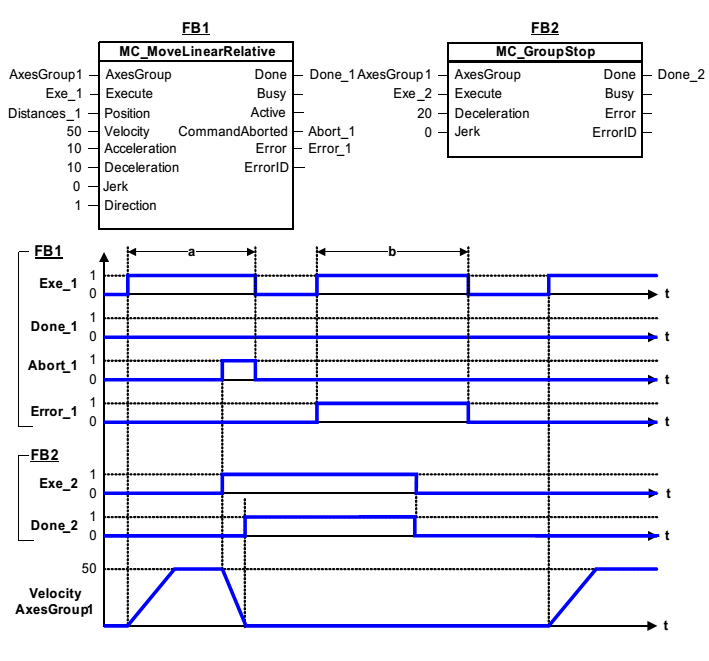
The example below shows the behavior in combination with a MC_MoveLinearRelative.
a) An axis group in linear movement is ramped down with MC_GroupStop. The group stops on the original path.
b) The axis group rejects motion commands as long as MC_GroupStop parameter “Execute” = TRUE. FB MC_MoveLinearRelative reports an error indicating the busy MC_GroupStop command. This error is an FB error, so the group is not moving to the state GroupErrorStop.
At the third “Exe1” rising edge, the group starts the next movement.
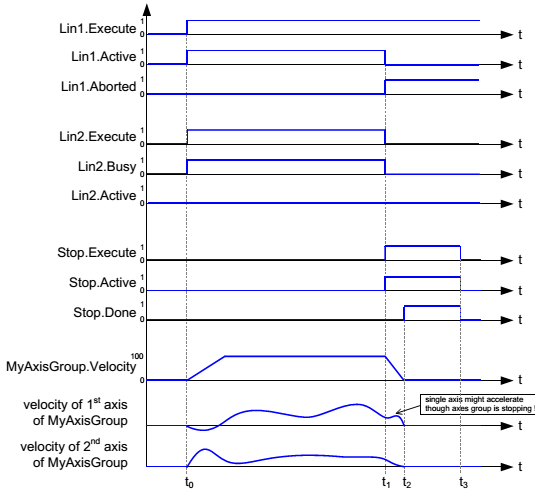
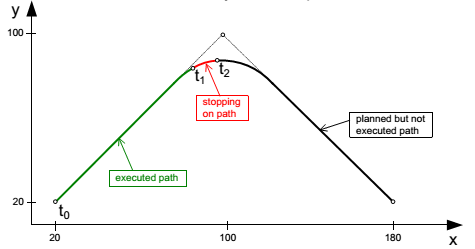
The following example demonstrates the behavior of MC_GroupStop in combination with two MC_MoveLinearAbsolute which are blended with defined constant path velocity:
t0) Two FBs MC_MoveLinearAbsolute are commanded on the axis group MyAxesGroup. The first FB becomes active immediately and MyAxesGroup starts to move from its actual position (20.0; 20.0) towards the first target position.
t1) Shortly after the tool center point has started to move on the blending contour blending Lin1 into Lin2, an FB MC_GroupStop is sent in the buffer mode mcAborting. The state of the axis group changes from GroupMoving to GroupStopping. MyAxesGroup decelerates until the velocity is zero, while the endpoint of the group stays on the contour.
NOTE: Though the path velocity of MyAxesGroup decreases continuously while stopping, single axis of the group might accelerate between the start of the deceleration and the stop of the group, due to the given path and kinematic transformation of MyAxesGroup.
t2) MyAxesGroup comes to standstill. The Done output of the FB MC_GroupStop is set. Since the Execute input of the FB MC_GroupStop is still set, the group stays in the state GroupStopping.
t3) The Execute input of the FB MC_GroupStop is reset. All outputs of the FB MC_GroupStop are reset. The group state changes to GroupStandby.
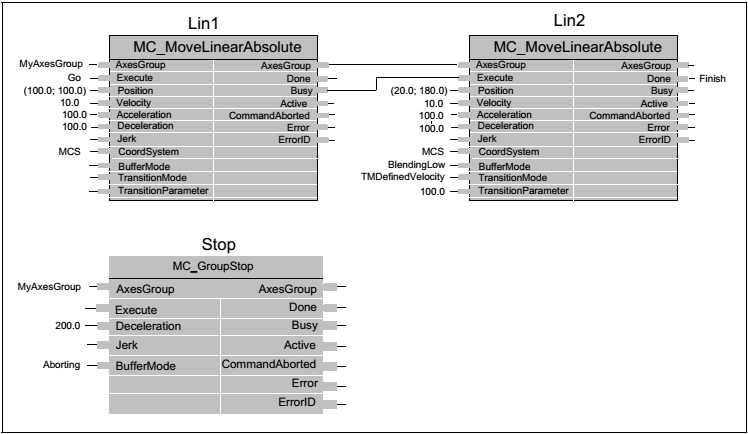
Path of MyAxesGroup
Example of MC_GroupStop in combination with two MC_MoveLinearAbsolute