Provides data access to the device through Service Data Object (SDO). The SDO settings for the axis and I/O module are the same.
Topics:
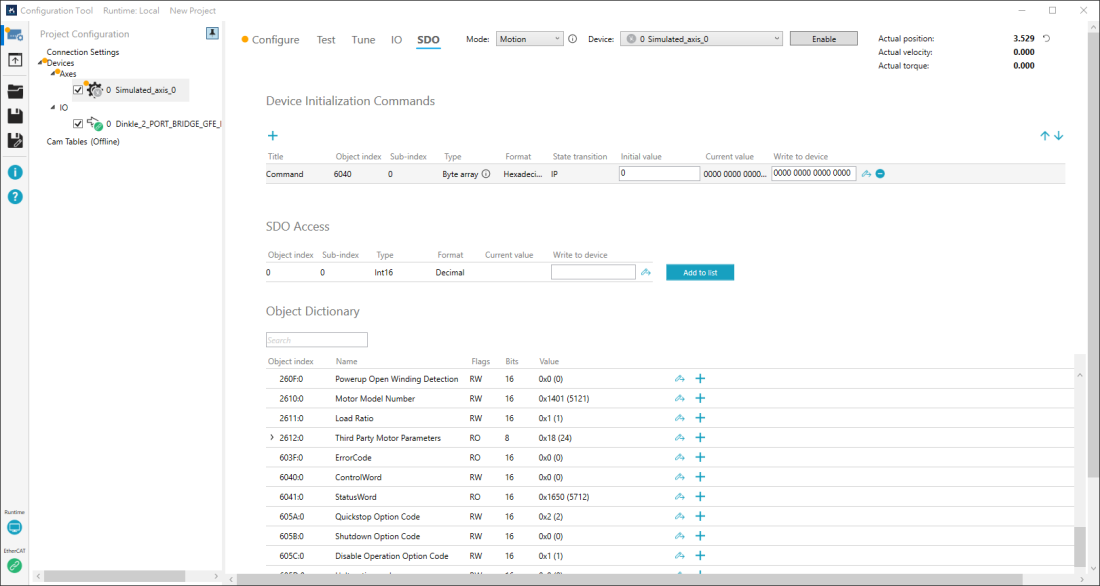
Device Initialization Commands
The initial commands of SDO that runs every time the hardware connects to KINGSTAR. You can add SDO objects to this area. Press ![]() to add an empty object. Every column of the object is editable. To edit, double-click the empty space or text in the field. After you enter the value, press Enter.
to add an empty object. Every column of the object is editable. To edit, double-click the empty space or text in the field. After you enter the value, press Enter.
Title: the name of the object.
Object index: the index of an object.
Sub-index: the index of an entry.
Type: the data type of the object. Types: String, Byte array, Byte, SByte, UInt16, Int16, UInt32, Int32, Single. The range of the type will be displayed after you make a selection. If you select Byte array, here's how to enter the value:
- Decimal format: The value should be a series of space-separated numbers. For example: 125 3 20 5
- Hexadecimal format: Each byte is represented by two hexadecimal characters. For example: 7D031405. Spaces between bytes are optional, as shown here: 7D 03 14 05 or 7D03 1405
Format: the format of the value that is read from or to be written into the object. It's Decimal or Hexadecimal.
State transition: specifies the EtherCAT transition state when a command is sent during the transition process. Three transition states are specified: IP, PS and SO.
- IP: a command is sent after the device transitions from the Init sate to the PreOP state, indicating that the sending occurs during the PreOP state.
- PS: a command is sent immediately before the device transitions from the PreOP state to the SafeOP state, indicating that the sending occurs during the PreOP state.
- SO: a command is sent immediately before the device transitions from the SafeOP state to the OP state, indicating that the sending occurs during the SafeOP state.
NOTE: EtherCAT states may change due to different operating methods. Here are two major scenarios.
- If you use the KINGSTAR Configuration Tool to establish an EtherCAT connection by clicking the Connect button on the Connection Settings page, all devices will transition to the OP state. Subsequently, if the Configuration Tool detects discrepancies between the connected devices and those listed in the project file, the Device Matching process will be initiated. After completing the Device Matching process, the Configure Tool will then revert the state of the devices to PreOP or SafeOP to send any necessary initialization commands. Once the commands are sent, all devices will transition back to the OP state.
- If you use KINGSTAR APIs to establish an EtherCAT connection with a Configuration Tool project file, the KINGSTAR Runtime will directly transition the devices from the Init state to the OP state and will send the initialization commands during this transition. The Device Matching process will be omitted in this case.
Initial value: the initial value of the object. If you want the device to use a value every time it connects to KINGSTAR, you can use this to assign the value.
Current value: the current value of the object. Use Write to device to edit this field.
Write to device: the value to be written into the object. After you enter the value, click ![]() .
.
Delete ( ): deletes the command.
): deletes the command.
SDO Access
Reads and writes the SDO object that is not listed in the object dictionary. The objects that are not listed in the object dictionary may be contained in firmware. You can access these objects here. Every column in SDO Access is editable. Double-click each of them to edit the value.
Object index: the index of the object.
Sub-index: the index of the entry.
Type: the data type of the object. Types: String, Byte array, Byte, SByte, UInt16, Int16, UInt32, Int32, Single. You must know the correct type to read or write the value.
Format: the format of the value that is read from or to be written into the object. It's Decimal or Hexadecimal.
Current value: the current value of the object. Use Write to device to edit this field.
Write to device: the value to be written into the object or its entry. After you enter the value, press the Write icon (![]() ) to write.
) to write.
Add to list: adds this item to Device Initialization Commands.
Object Dictionary
The object dictionary retrieved from an ESI file.
Search box: when the object dictionary is long, you can use the search box to quickly find the object you want. Type the object's index or name to filter the result. Note that the search box can't find the entry of the object (subitem).
Object index: the index of an object.
Name: the name of the object.
Flags: the read and write permission of the object.
Value: the value read from or to be written into the device. Value types: Decimal or Hexadecimal. The value starts with 0x is hexadecimal; the value in parenthesis is decimal.
Write (![]() ): opens the Set Value dialog box.
): opens the Set Value dialog box.
Blue plus (![]() ): adds the object to Device Initialization Commands.
): adds the object to Device Initialization Commands.
Set value
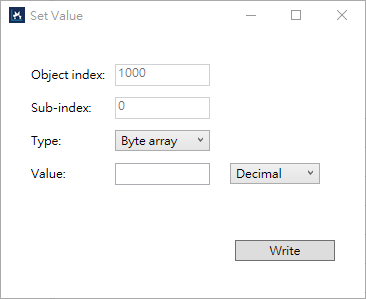
Object index: the index of an object.
Sub-index: the index of an entry.
Type: the data type of the object or its entry. Typically you don't need to change this because the correct type is selected for you, unless the information in the ESI file is not correct.
Value: the value to be written. Format can be Decimal or Hexadecimal.
Write: writes the value.
See also